Find Out How to Engage in Whole Brain Thinking
The HBDI Whole Brain Thinking Model or Herrmann Brain Dominance Instrument is a metaphorical model used to understand that each person has four quadrants when it comes to the process of thinking, communicating, and decision making.
The below one-sentence tips share 31 ways in which we can all benefit by considering beyond our own thinking preferences and engaging in whole-brain thinking:
Tips 1-10
- 1. For each big task or project you have, consider each quadrant for solutions, perspectives, and approaches.
- 2. If frustration is building within the team, step back and walk around the 4 quadrants, gain the facts around it, the feelings it brings, the future impact, and then the steps to resolve it.
- 3. Give feedback in a Blue way:
- Be precise & logical, use facts, and pay attention to data.
- 4. Give feedback in a Green way:
-
- Structure in a sequential approach and pay attention to details.
-
- 5. Give feedback in a Red way:
-
-
- Be empathic and caring, use eye contact, and pay attention to feelings.
-
-
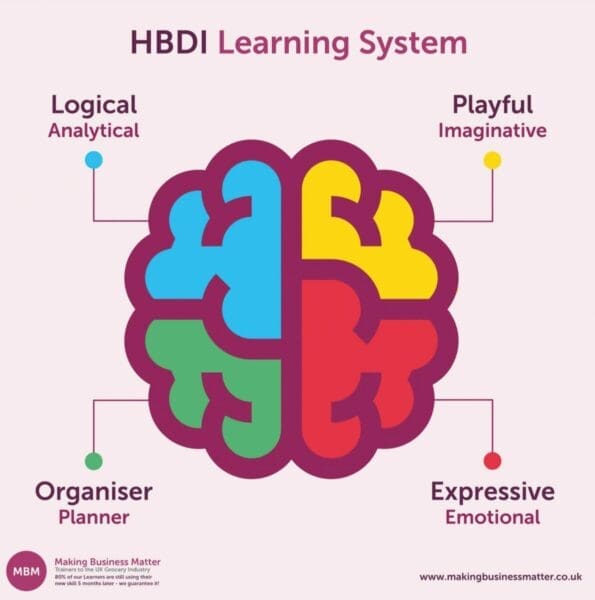
- 6. Give feedback in a Yellow way:
-
-
-
- Be imaginative & holistic, use metaphors, and pay attention to the ultimate outcomes.
-
-
-
- 7. Consider activities to form new habits, that strengthen your least preferred thinking style by doing them.
- 8. Being able to apply a little HBDI information is much better than understanding a lot.
- 9. Famous people; Blue – Bill Gates, Green – Queen Elizabeth 2, Red – Mother Theresa, and Yellow – Einstein.
- 10. Utilise the brains around you by gaining the perspective and thoughts of your colleagues to solve a challenge.
(Click on the image for a full size version.)
Tips 11-20
- 11. This Ultimate Infographic for HBDI will tell you more.
- 12. Expectations of your audience in the Blue:
- Focus on the facts, answer the ‘what’, and ensure you have technical accuracy & the chance for debate.
- 13. Expectations of your audience in the Green:
- Unfold your topic step by step, stick to timings before during, and after, keep it low risk.
- 14. Expectations of your audience in the Red:
- Have consideration for their needs & feelings, explore the involvement of people and allow for group discussion.
- 15. Expectations of your audience in the Yellow:
- Provide the overview & future benefits, use visuals, metaphors and allow for flexibility.
- 16. Work with your brain, tackle tasks that require your lower preferences quadrants when you have your highest energy levels.
- 17. If you had your time again on an issue, walk around the quadrants and consider what you would do differently.
- 18. Decision making from the Blue:
- What is the decision and what are the facts?
- 19. Decision making from the Green:
- How are you going to make the decision and manage the risks?
- 20. Decision making from the Red:
- Who is involved in the decision and who will it impact on?
- Check out ‘The Whole Brain Business Book.’

Tips 21-28
- 21. Decision making from the Yellow:
- Why are you making the decision and why is it important?
- 22. Hard decision to make? Discuss with your team how they would solve it for an understanding of their perspectives.
- 23. Is your audience preferred thinking style unknown? Put a tick in each of the quadrants to increase your chances of engagement.
- 24. Replying to an email or in conversation, consider what colour they are, and then reply in a way to be more like them.
- 25. Problem-solving in a Blue Way:
- State the problem, now consider what you can – take away, + add to, x multiple or ÷ divide by to reach a solution?
- 26. Problem-solving in a Green Way:
- State the problem, then consider a story or previous experience with a similar desired outcome, explore the steps taken then and how it was solved.
- 27. Problem-solving in a Red Way:
- State the problem, then consider how someone else may solve it, this could be a colleague, tv personality or famous person from history.
- 28. Problem-solving in a Yellow Way:
- State the problem, pick a superhero, consider their superpower, how would they use that to solve it, then bring it back to the real world and translate your idea.

Tips 29-31
- 29. Remember this story; Sue said to Roy, ‘Do you love me still?’, and Roy replied, ‘I told you on our wedding day that I loved you, and if that changes I will let you know’. A red to a green helps understand the two different perspectives.
- 30. By being aware of your own colour you will firstly become more aware, secondly more tolerant of others, and thirdly start to use the power of others.
- 31. Each of the colours is a witness at a car accident being questioned by the Police:
- Blue – ‘The red Ford and the blue Vauxhall hit at 10.26 pm.’
- Green – ‘Firstly, this car was driving up this road, and then hit the second car and ended up in the ditch over there’.
- Yellow – ‘We really need to sort out accidents on this road because there are too many’.
- Red – ‘This lady was crying when her vehicle stopped. She has a child in the car, and that guy was in the wrong’.
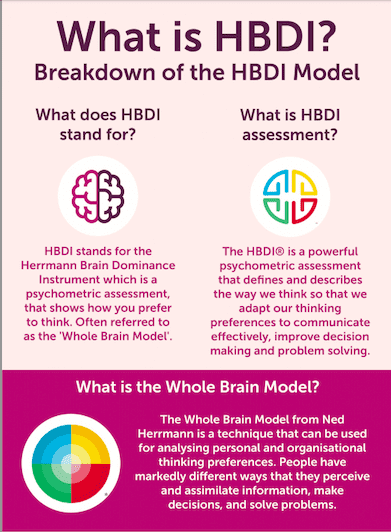
What is HBDI? Find out more here in our Ultimate Guide to HBDI.





