Understanding MBTI Categories for Personal and Professional Development
Navigating the complexities of human personalities is a challenge in both personal and professional arenas. Luckily, the Myers Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) has offered a significant breakthrough in understanding these complexities. This article provides a comprehensive look at the 16 MBTI personalities, their strengths and weaknesses, and their implications for the workplace. Furthermore, you can take the MBTI categories quiz to discover your personality type today.
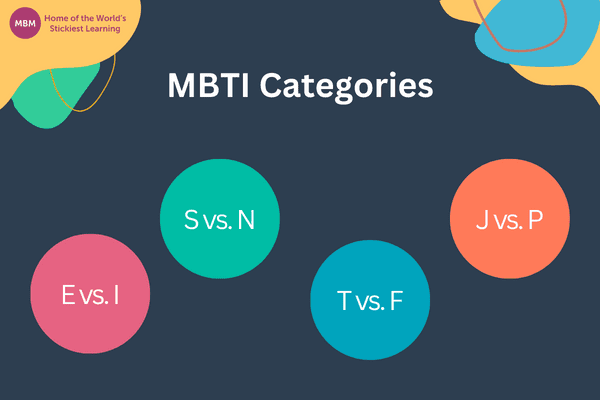
The 4 MBTI Categories
Before delving into the rich tapestry of the 16 MBTI personality types, it’s crucial to understand the foundational four categories that these types are built upon. Note that these categories encapsulate the core dynamics of our personalities. That is, how we interact with the world, process information, make decisions, and structure our lives. The 4 categories are:
Extraversion (E) Vs. Introversion (I)
This category is about where individuals draw their energy from. Basically, extroverts are energised by social interaction, while introverts gain energy from solitary activities or intimate interactions.
Sensing (S) Vs. Intuition (N)
This dichotomy is about how individuals gather and interpret information. Basically, sensing types are pragmatic and focus on concrete facts and details, while intuitive types prefer abstract concepts and look for patterns and possibilities.
Thinking (T) Vs. Feeling (F)
This category is about how individuals make decisions. In summary, thinking types base their decisions on objective analysis and logic while feeling types consider the emotional impact and harmony in their decision-making process.
Judging (J) Vs. Perceiving (P)
Lastly, this dichotomy is about how individuals approach the outside world. Judging types prefer structure and decided courses while perceiving types maintain openness and flexibility.
Each of the 16 MBTI types is a combination of these four categories, resulting in a unique blend of traits that defines each personality type.
Here’s How the 16 Types are Split Into Four MBTI Categories:
Extraversion (E) Vs. Introversion (I)
Extraverted types: ESTJ, ESFJ, ENFJ, ENTJ, ESTP, ESFP, ENFP, ENTP.
Introverted types: ISTJ, ISFJ, INFJ, INTJ, ISTP, ISFP, INFP, INTP.
Sensing (S) Vs. Intuition (N)
Sensing types: ESTJ, ESFJ, ISTJ, ISFJ, ESTP, ESFP, ISTP, ISFP.
Intuitive types: ENFJ, ENTJ, INFJ, INTJ, ENFP, ENTP, INFP, INTP.
Thinking (T) Vs. Feeling (F)
Thinking types: ESTJ, ENTJ, ISTJ, INTJ, ESTP, ENTP, ISTP, INTP.
Feeling types: ESFJ, ENFJ, ISFJ, INFJ, ESFP, ENFP, ISFP, INFP.
Judging (J) Vs. Perceiving (P)
Judging types: ESTJ, ESFJ, ENFJ, ENTJ, ISTJ, ISFJ, INFJ, INTJ.
Perceiving types: ESTP, ESFP, ENFP, ENTP, ISTP, ISFP, INFP, INTP.
In essence, having a nuanced understanding of the MBTI categories paves the way for an in-depth exploration of the 16 unique Myers-Briggs personality types. Each type is a unique combination of the four category dichotomies, offering a comprehensive personality profile that provides valuable insights into an individual’s preferred way of interacting with the world, processing information, making decisions, and approaching structure and planning.
The 16 MBTI Categories: A Comprehensive Overview
The 16 personality types or MBTI categories, from ISTJ to ENFP, each bring their own strengths, weaknesses, and tendencies to the table. And understanding these can significantly improve both personal development and professional team dynamics. Particularly, each type is associated with a certain set of preferences and behaviours, providing a valuable framework for understanding and predicting how individuals are likely to respond in different situations.
Now, let’s delve into the rich tapestry of the 16 MBTI personality types, understanding the unique characteristics, strengths, and weaknesses that each type brings to the world. Additionally, we’ll be exploring how these traits can be effectively leveraged in a professional environment.
1. ISTJ – The Inspector
ISTJs, often referred to as Inspectors, are characterised by their practicality, reliability, and attention to detail. Moreover, they value structure and order, making them excellent planners and organisers.
ISTJ Strengths
- Dependable: ISTJs are known for their reliability and dedication to their responsibilities.
- Logical: They approach problems with a logical and methodical mindset.
- Efficient: They are excellent at creating and maintaining systems and procedures.
ISTJ Weaknesses
- Rigid: Their preference for routine can make them resistant to change.
- Overly analytical: They may overlook the emotional aspect of situations.
- Private: They can appear aloof as they’re not naturally expressive.
Workplace Implications
ISTJs are the backbone of any organisation. In short, their meticulousness and dedication make them excellent in roles that require attention to detail and consistency, such as finance, project management, and logistics.
2. ISFJ – The Protector
ISFJs, or Protectors, are warm, considerate, and dedicated individuals who prioritise harmony and cooperation. Basically, they are diligent and thorough in their work, often going above and beyond their duties.
ISFJ Strengths
- Caring: ISFJs have a strong desire to help and support others.
- Observant: They are attentive to details and sensitive to the needs of others.
- Practical: They excel at tasks that require practical skills and common sense.
ISFJ Weaknesses
- Reluctant to change: They may struggle when situations require flexibility and adaptability.
- Overly accommodating: They may neglect their own needs to please others.
- Difficulty with conflict: They may avoid confrontation, even when necessary.
Workplace Implications
ISFJs thrive in supportive roles, where their natural inclination to help can shine. Moreover, their meticulous nature and strong work ethic make them excellent in healthcare, social work, and administrative roles.
3. INFJ – The Counsellor
INFJs, known as Counsellors, are insightful, empathetic individuals with a deep understanding of people and a vision for making the world better.
INFJ Strengths
- Insightful: They have a unique ability to understand complex issues and human motives.
- Compassionate: They genuinely care about others and are often found helping people.
- Visionary: They can see potential and create a clear vision for the future.
INFJ Weaknesses
- Sensitive: They may take criticism personally and get upset by harsh words.
- Perfectionistic: They may set unrealistically high standards for themselves and others.
- Private: They can be difficult to get to know and require significant time alone.
Workplace Implications
INFJs are often found in careers that allow them to express their creativity and help others, such as writing, counselling, and non-profit work. Their ability to understand and connect with others makes them excellent team leaders.
4. INTJ – The Mastermind
INTJs, also known as Masterminds, are strategic, analytical, and objective. Specifically, they have a keen interest in improving systems and processes with their innovative ideas.
INTJ Strengths
- Strategic: They excel at identifying inefficiencies and formulating plans to improve them.
- Independent: They are self-reliant and prefer to work on their own.
- Visionary: They have a knack for seeing possibilities for improvement.
INTJ Weaknesses
- Overly analytical: They may overlook the emotional aspect of situations.
- Private: They can be reserved and hard to get to know.
- Stubborn: They can be set in their ways and resistant to other perspectives.
Workplace Implications
INTJs thrive in intellectually stimulating environments where they can implement their innovative ideas. Their analytical nature makes them excellent in research, engineering, and strategic planning roles.
5. ISTP – The Craftsman
ISTPs, known as Craftsmen, are practical, observant, and cool under pressure. Basically, they enjoy hands-on activities and live in the moment, often thriving in crisis situations.
ISTP Strengths
- Adaptable: They are flexible and open-minded, easily adjusting to new situations.
- Problem-solving: They excel at understanding how things work and finding practical solutions.
- Unflappable: They remain calm and composed under stress.
ISTP Weaknesses
- Impulsive: They may take risks without considering the consequences.
- Private: They tend to keep their feelings to themselves and can be difficult to get to know.
- Easily bored: They may lose interest if tasks become routine or tedious.
Workplace Implications
ISTPs excel in roles that require hands-on problem-solving and quick decision-making, such as mechanics, engineers, or emergency medical technicians.
6. ISFP – The Composer
ISFPs, referred to as Composers, are warm, sensitive, and dedicated to their values. Furthermore, they are artistic, enjoy exploring the world around them, and find beauty in everyday experiences.
ISFP Strengths
- Empathetic: They have a strong ability to understand and relate to others’ feelings.
- Adaptable: They are flexible and open to new experiences.
- Creative: They have a keen aesthetic sense and can create beautiful works of art.
ISFP Weaknesses
- Avoidant: They tend to avoid conflict and confrontation.
- Sensitive: They may take criticism personally and become easily overwhelmed by negative situations.
- Unpredictable: Their desire for spontaneity can make them seem unreliable.
Workplace Implications
ISFPs thrive in roles that allow them to express their creativity and work at their own pace, such as artists, designers, or counsellors.
7. INFP – The Healer
INFPs, also known as Healers, are idealistic, compassionate, and dedicated to their values. Importantly, they strive to help others and make the world a better place.
INFP Strengths
- Idealistic: They have a strong sense of purpose and work towards their ideals.
- Empathetic: They understand and relate to other’s feelings.
- Creative: They have a rich imagination and can see potential in everything.
INFP Weaknesses
- Overly idealistic: They may become disappointed when reality does not meet their expectations.
- Sensitive: They may take things personally and become easily stressed.
- Difficult to get to know: They can be reserved and require significant time alone.
Workplace Implications
INFPs are often drawn to careers that align with their values and allow them to help others, such as psychology, writing, or non-profit work.
8. INTP – The Architect
INTPs, known as Architects, are logical, creative, and curious. They enjoy exploring new ideas and seeking understanding.
INTP Strengths
- Analytical: They excel at logical reasoning and can quickly understand complex concepts.
- Creative: They are innovative thinkers with a rich imagination.
- Independent: They are self-reliant and comfortable spending time alone.
INTP Weaknesses
- Overly analytical: They may overlook the emotional aspect of situations.
- Detached: They can seem aloof and indifferent to others.
- Uncertain: They may second-guess their decisions and struggle to make choices.
Workplace Implications
INTPs excel in roles that allow them to use their analytical and creative thinking, such as scientists, engineers, or programmers.
9. ESTP – The Dynamo
ESTPs, or Dynamos, are energetic, practical, and observant. Basically, they thrive on excitement and are quick to respond to immediate needs.
ESTP Strengths
- Pragmatic: They are realistic and practical in their approach to solving problems.
- Observant: They notice physical details and changes in their environment.
- Energetic: They enjoy staying active and are usually enthusiastic and lively.
ESTP Weaknesses
- Impulsive: They tend to take action without considering the consequences.
- Unstructured: They dislike routine and prefer to keep their options open.
- Risk-takers: They enjoy the excitement and can engage in risky behaviour.
Workplace Implications
ESTPs are well-suited to roles that require quick thinking and action, such as sales, marketing, or emergency services.
10. ESFP – The Performer
ESFPs, known as Performers, are outgoing, friendly, and enjoy being the centre of attention. Furthermore, they are observant and practical, preferring to live in the moment.
ESFP Strengths
- Sociable: They enjoy being around people and are often the life of the party.
- Observant: They are very aware of their surroundings and the needs of others.
- Practical: They prefer concrete information and real-world problems.
ESFP Weaknesses
- Easily bored: They may lose interest if tasks become routine or tedious.
- Sensitive: They may take criticism personally and become easily overwhelmed.
- Impulsive: They can make hasty decisions without considering the long-term consequences.
Workplace Implications
ESFPs thrive in roles that allow them to interact with others and solve practical problems, such as customer service, hospitality, or healthcare.
11. ENFP – The Champion
ENFPs, also known as Champions, are enthusiastic, creative, and value-driven. Also, they are excellent communicators and enjoy helping others realise their potential.
ENFP Strengths
- Empathetic: They have a strong ability to understand and relate to other’s feelings.
- Creative: They are innovative thinkers with a rich imagination.
- Enthusiastic: They are often optimistic and full of energy.
ENFP Weaknesses
- Overly emotional: They can become overly invested in their personal relationships.
- Unfocused: They may struggle to stick to one thing for long periods.
- Stress-sensitive: They can become overwhelmed when faced with criticism or conflict.
Workplace Implications
ENFPs are well-suited to roles that allow them to express their creativity and work with people, such as counselling, teaching, or public relations.
12. ENTP – The Visionary
ENTPs, known as Visionaries, are innovative, curious, and intellectually quick. They enjoy debating ideas and exploring various options.
ENTP Strengths
- Innovative: They are excellent problem-solvers and enjoy coming up with new ideas.
- Charismatic: They are typically outgoing and good at influencing others.
- Analytical: They are skilled at understanding complex theories and systems.
ENTP Weaknesses
- Argumentative: They may enjoy debating ideas a bit too much, which can lead to unnecessary conflict.
- Insensitive: They might overlook the feelings of others when they get too caught up in their ideas.
- Prone to boredom: They may struggle to follow through with tasks once the initial excitement wears off.
Workplace Implications
ENTPs thrive in environments that allow them to innovate and engage in intellectual debates. As a result, they do well in entrepreneurial roles or as strategists, consultants, or engineers.
13. ESTJ – The Supervisor
ESTJs, also known as Supervisors, are practical, reliable, and efficient. They value tradition and order, and they have a keen sense for right and wrong.
ESTJ Strengths
- Organised: They excel in creating order and structure.
- Practical: They are realistic and prefer concrete, measurable objectives.
- Decisive: They are confident in their decisions and stick by them.
ESTJ Weaknesses
- Inflexible: They may struggle with new ideas that challenge established rules.
- Impersonal: They can overlook people’s feelings in favour of task completion.
- Impatient: They get frustrated with inefficiency and confusion.
Workplace Implications
ESTJs do well in roles that require organisation and clear decision-making, such as people management, administration, or law enforcement.
14. ESFJ – The Provider
ESFJs, known as Providers, are warm, cooperative, and value harmony. They are attentive to others’ needs and enjoy helping and supporting others.
ESFJ Strengths
- Supportive: They are good at providing practical help and emotional support.
- Reliable: They are dependable and follow through on their commitments.
- Observant: They are aware of others’ feelings and responsive to their needs.
ESFJ Weaknesses
- Overly accommodating: They may neglect their needs to please others.
- Averse to change: They might struggle with new methods and prefer familiar routines.
- Sensitive to criticism: They may take negative feedback personally.
Workplace Implications
ESFJs excel in roles where they can support and care for others, such as in healthcare, social work, or customer service.
15. ENFJ – The Teacher
ENFJs, also known as Teachers, are empathetic, responsive, and responsible. Furthermore, they are excellent communicators and are committed to achieving the common good.
ENFJ Strengths
- Inspiring: They are adept at motivating and inspiring others.
- Organised: They are skilled at planning and coordinating people and resources.
- Reliable: They are committed and follow through on their promises.
ENFJ Weaknesses
- Overly idealistic: They might have unrealistic expectations of others.
- Overly involved: They can become too invested in others’ problems.
- Struggle with conflict: They tend to avoid unpleasant situations and may struggle to make tough decisions.
Workplace Implications
ENFJs thrive in roles where they can help others grow and develop, such as teaching, coaching, or counselling.
16. ENTJ – The Commander
ENTJs, known as Commanders, are strategic, efficient, and objective. Specifically, they have a keen sense of improvement and a drive to achieve their goals.
ENTJ Strengths
- Efficient: They are highly organised and skilled at implementing plans.
- Strategic: They are excellent at seeing the bigger picture and setting long-term goals.
- Decisive: They are confident in their decision-making abilities.
ENTJ Weaknesses
- Stubborn: They may have difficulty accepting others’ ideas.
- Impersonal: They can overlook people’s feelings in favour of achieving objectives.
- Intolerant: They may dismiss ideas or people they perceive as inefficient.
Workplace Implications
ENTJs excel in roles that require strategic planning and assertive leadership, such as executives, managers, or entrepreneurs. All in all, they thrive in an environment where they can apply their logic and determination to reach objectives.
What Are the Rarest MBTI Types?
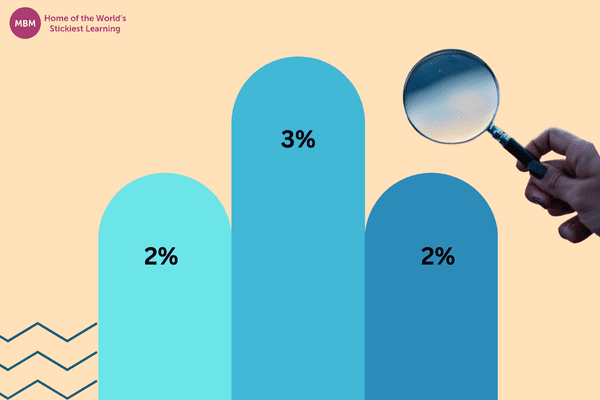
While the prevalence of each MBTI type can vary depending on many factors, there are certain types that are less commonly reported. Below, we explore three of the rarest MBTI types and offer some insight into why they might be less common.
INFJ – The Advocate
Regarded as the rarest MBTI type, INFJs make up below 2% of the population. They are known for their idealism, vision, and depth of compassion. Also, advocates are a combination of traits that don’t often occur together. That is, they’re both creative and driven, idealistic yet decisive.
ENTJ – The Commander
Commanders make up around 2% of the population. They are charismatic, assertive, and strategic, often landing in leadership roles. All in all, they’re driven by a desire to solve complex problems and take charge of making things happen.
INTP – The Architect
Architects are analytical, innovative, and deeply thoughtful individuals. They are often fascinated by logical analysis and complex systems. Additionally, they make up about 3% of the population.
Conclusion
Understanding the strengths, weaknesses, and workplace implications of each of these sixteen Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) personality types can help managers coach their teams more effectively. Specifically, by tailoring your coaching approach to each team member’s unique personality, you can foster stronger relationships, improve productivity, and lead more effectively.
But remember, these types are just a guide. People are complex and may not fit neatly into one category or another. So as a manager, it’s crucial to respect individual differences and adapt your management style accordingly.
Moreover, investing time in understanding your team’s personality types will pay dividends in terms of improved communication skills, increased understanding, and a more harmonious workplace. After all, a team that understands and appreciates each other’s strengths and weaknesses is a team that can truly excel.
By developing coaching skills and learning to adapt to the diverse personalities in your team, you can help each individual achieve their potential and contribute to your organisation’s success. So here’s to becoming a more understanding, adaptable, and effective leader!
Enjoyed this article? Check out our MBTI videos on our YouTube channel.




